Hey there, ladies and gents! So, I've decided to share my thoughts on the online pharmacy named FDA-approved-rx.net. Just to make things clear, this is not the usual online shop; they claim to sell FDA approved medicines at your doorstep. Interesting, huh? Therefore, I thought to dig into their offerings and services a little deeper. Join me as I unravel the truths and myths behind this online drugstore.
FDA-approved Rx Network
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of Kamagra, a popular alternative for managing erectile dysfunction. It explores what Kamagra is, its active ingredient Sildenafil Citrate, and the process of purchasing it online. Readers will find insights into the medical perspectives, potential side effects, drug interactions, and dosage recommendations. The article provides useful tips and interesting facts about Kamagra, offering readers valuable information in their quest to understand and possibly utilize this medication.
Hi there! It's always a journey, managing my blood pressure with enalapril-hydrochlorothiazide. In this post, I'm sharing my experiences and tips on how we can overcome common challenges faced during treatment. From dealing with side effects, to maintaining consistency with our medication, let's explore solutions together. Join me in navigating our health journey with a positive attitude.
As someone with kidney issues, I always found it crucial to fully understand my treatments, especially medications like Nebivolol. In today's post, we're diving into how Nebivolol interacts with kidney function-why it's essential to know. We'll chat about the risks and benefits, and find answers to those frequently occurring questions many of you have about Nebivolol and kidney disease. It's all about empowering you to take charge of your health, particularly when dealing with kidney ailments. After all, knowledge is power, isn't it?
Hi everyone! Today, I'm going to shed some light on a topic that we don't discuss often but is crucial for our health - the impact of fungal infections on our joint health and mobility. We'll delve into how these pesky infections can wreak havoc on our joints, leading to discomfort, reduced mobility, and in severe cases, debilitating diseases. Moreover, we'll explore the signs to watch out for and the steps we can take towards safeguarding our joint health. Join me in this enlightening journey towards a healthier you.
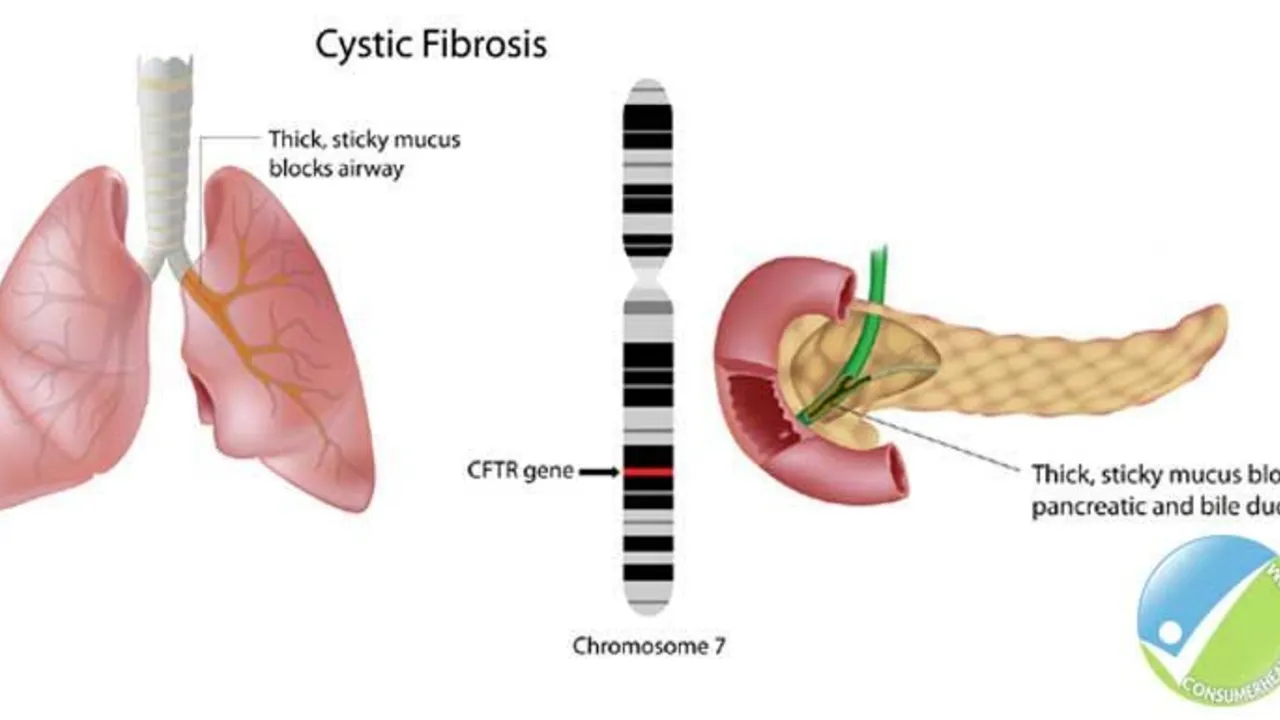
The Role of Ursodeoxycholic Acid in the Management of Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease
Hello ladies and gents, today let's discuss something crucial related to Cystic Fibrosis (CF). Our focus will be on the role of Ursodeoxycholic Acid in managing CF-Related Liver Disease. This medicine has been known to significantly enhance liver function in people with CF, giving them a better fighting chance. We will delve deep into how it works, its benefits, and potential side effects. So, join me in exploring this life-changing topic in an easy-to-understand and relatable way!
Hi there, it's from your gal pal again. Today, I'll be shedding light on the interplay between hearing loss and that annoyance called ringing in the ears, often known as tinnitus. We'll be exploring causes, the interconnectedness of these two auditory issues, and potential treatments. Let's decode the sounds, or lack thereof, our ears make and help you better understand your auditory health. Make sure to stay tuned, because this is an aspect of our health that we often overlook!
The Ergot Revolution: How This Dietary Supplement is Transforming Health and Wellness
Hi there, in today's blog post I'm going to share some fascinating insights on what's shaking up the health and wellness scene - the Ergot Revolution. We'll discuss how this dietary supplement is making waves by considerably improving health and transforming wellness practices globally. I'll dive into the secrets behind its rising popularity and provide a balanced look at its potential benefits. So, stay tuned if you're keen to make a healthy pivot in your life!